Uttarakhand Board of School Education (UBSE) has outlined the Physics syllabus for Class 12th (twelfth) students for the academic year 2024-2025. The syllabus is structured to provide students with a deep understanding of the principles of Physics, crucial for both academic progression and competitive examinations.
Check UBSE class 12th Physics syllabus 2024 along with in-depth physics examination pattern for Uttarakhand board examination 2024-2025.
Contents
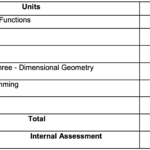
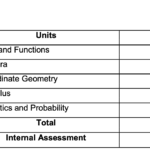
Uttarakhand Board Class 12th Physics Syllabus 2024-2025
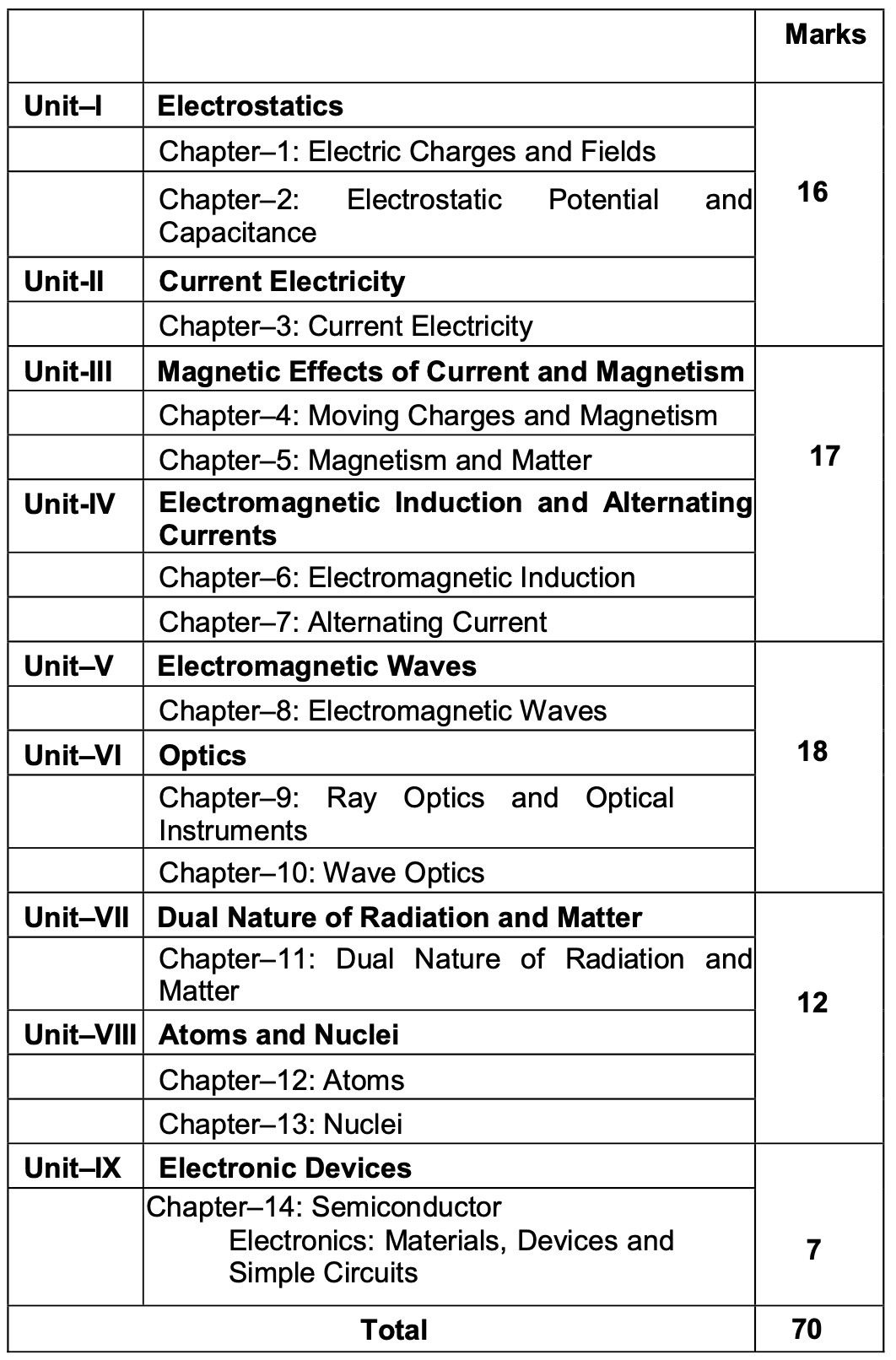
Unit 1 : Electrostatics
Chapter–1: Electric Charges and Fields: Electric charges, Conservation of charge, Coulomb’s law-force between two- point charges, forces between multiple charges; superposition principle and continuous charge distribution.
Electric field, electric field due to a point charge, electric field lines, electric dipole, electric field due to a dipole, torque on a dipole in uniform electric field.
Electric flux, statement of Gauss’s theorem and its applications to find field due to infinitely long straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet and uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside).
Chapter–2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance: Electric potential, potential difference, electric potential due to a point charge, a dipole and system of charges; equipotential surfaces, electrical potential energy of a system of two-point charges and of electric dipole in an electrostatic field.
Conductors and insulators, free charges and bound charges inside a conductor. Dielectrics and electric polarisation, capacitors and capacitance, combination of capacitors in series and in parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with and without dielectric medium between the plates, energy stored in a capacitor (no derivation, formulae only).
Unit : 2 Current Electricity
Chapter–3: Current Electricity: Electric current, flow of electric charges in a metallic conductor, drift velocity, mobility and their relation with electric current; Ohm’s law, V-I characteristics (linear and non-linear), electrical energy and power, electrical resistivity and conductivity, temperature dependence of resistance, Internal resistance of a cell, potential difference and emf of a cell, combination of cells in series and in parallel, Kirchhoff’s rules, Wheatstone bridge.
Unit : 3 Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Chapter–4: Moving Charges and Magnetism:- Concept of magnetic field, Oersted’s experiment.
Biot – Savart law and its application to current carrying circular loop.
Ampere’s law and its applications to infinitely long straight wire. Straight solenoid (only qualitative treatment), force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields.
Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field, force between two parallel current-carrying conductors-definition of ampere, torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment, moving coil galvanometer- its current sensitivity and conversion to ammeter and voltmeter.
Chapter–5: Magnetism and Matter: Bar magnet, bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis (qualitative treatment only), torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field (qualitative treatment only), magnetic field lines.
Magnetic properties of materials- Para-, dia- and ferro-magnetic substances with examples, Magnetisation of materials, effect of temperature on magnetic properties.
Unit : 4 Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Chapter–6: Electromagnetic Induction:- Electromagnetic induction; Faraday’s laws, induced EMF and current; Lenz’s Law, Self and mutual induction.
Chapter–7: Alternating Current: Alternating currents, peak and RMS value of alternating current/voltage; reactance and impedance; LCR series circuit (phasors only), resonance, power in AC circuits, power factor, wattless current. AC generator, Transformer.
Unit : 5 Electromagnetic waves
Chapter–8: Electromagnetic Waves:- Basic idea of displacement current, Electromagnetic waves, their characteristics, their transverse nature (qualitative idea only).
Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays) including elementary facts about their uses.
Unit : 6 Optics
Chapter–9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments:- Ray Optics: Reflection of light, spherical mirrors, mirror formula, refraction of light, total internal reflection and optical fibers, refraction at spherical surfaces, lenses, thin lens formula, lens maker’s formula, magnification, power of a lens, combination of thin lenses in contact, refraction of light through a prism.
Optical instruments: Microscopes and astronomical telescopes (reflecting and refracting) and their magnifying powers.
Chapter–10: Wave Optics:- Wave optics: Wave front and Huygen’s principle, reflection and refraction of plane wave at a plane surface using wave fronts. Proof of laws of reflection and refraction using Huygen’s principle. Interference, Young’s double slit experiment and expression for fringe width (No derivation final expression only), coherent sources and sustained interference of light, diffraction due to a single slit, width of central maxima (qualitative treatment only)
Unit : 7 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Chapter–11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter:- Dual nature of radiation, Photoelectric effect, Hertz and Lenard’s observations; Einstein’s photoelectric equation-particle nature of light. Experimental study of photoelectric effect
Matter waves-wave nature of particles, de-Broglie relation.
Unit : 8 Atoms and Nuclei
Chapter–12: Atoms:- Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford’s model of atom; Bohr model of hydrogen atom, Expression for radius of nth possible orbit, velocity and energy of electron in nth orbit, hydrogen line spectra (qualitative treatment only).
Chapter–13: Nuclei:- Composition and size of nucleus, nuclear force
Mass-energy relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon and its variation with mass number; nuclear fission, nuclear fusion.
Unit : 9 Electronic Devices
Chapter–14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits: Energy bands in conductors, semiconductors and insulators (qualitative ideas only) Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors- p and n type, p-n junction
Semiconductor diode – I-V characteristics in forward and reverse bias, application of junction diode -diode as a rectifier.
Uttarakhand Board Physics Class 12 Practical Exam Syllabus
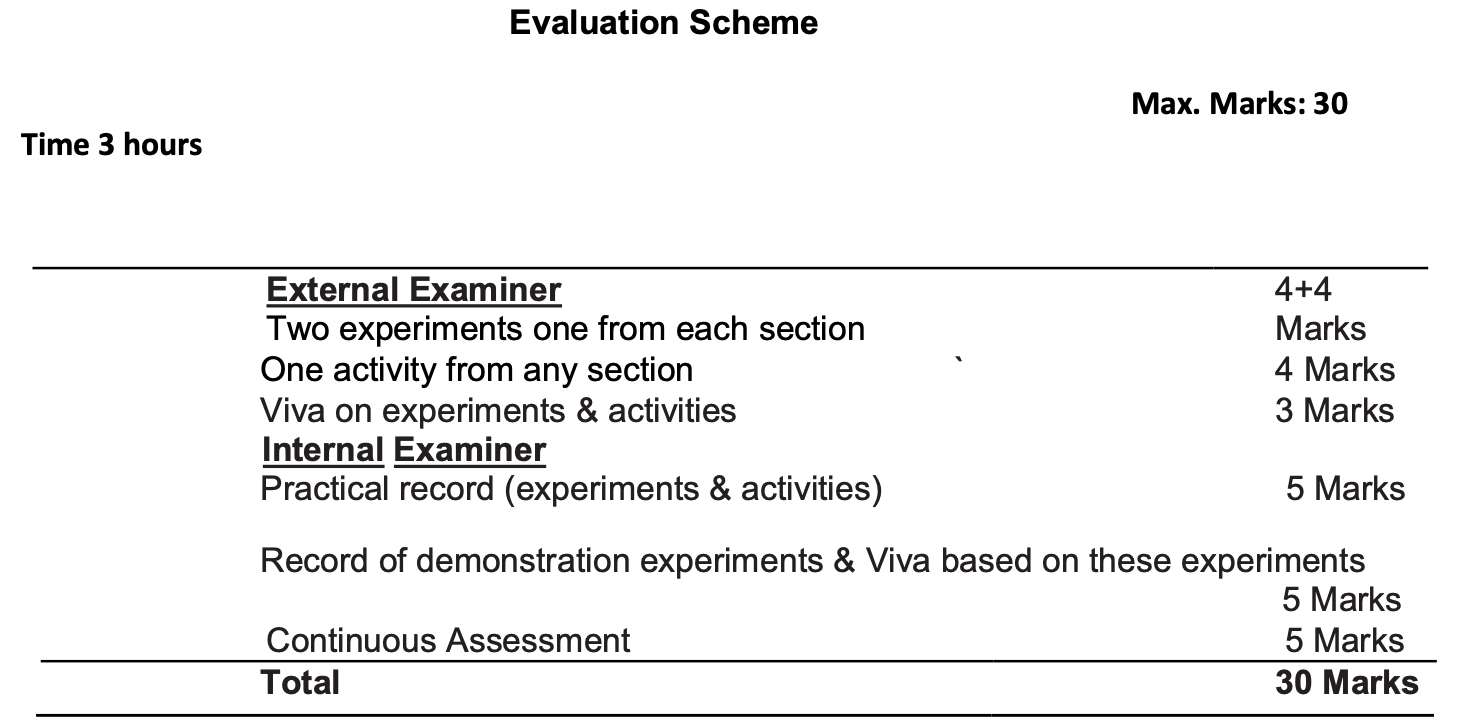
Experiments SECTION–A
- To determine resistivity of two / three wires by plotting a graph for potential difference versus current.
- To find resistance of a given wire / standard resistor using metre bridge.
- To verify the laws of combination (series) of resistances using a metre bridge.
OR
- To verify the laws of combination (parallel) of resistances using a metre bridge.
- To determine resistance of a galvanometer by half-deflection method and to find its figure of merit.
- To convert the given galvanometer (of known resistance and figure of merit) into a voltmeter of desired range and to verify the same.
OR
- To convert the given galvanometer (of known resistance and figure of merit) into an ammeter of desired range and to verify the same.
- To find the frequency of AC mains with a sonometer.
Activities
- To measure the resistance and impedance of an inductor with or without iron core.
- To measure resistance, voltage (AC/DC), current (AC) and check continuity of a given circuit using multimeter.
- To assemble a household circuit comprising three bulbs, three (on/off) switches, a fuse and a power source.
- To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit.
- To study the variation in potential drop with length of a wire for a steady current.
- To draw the diagram of a given open circuit comprising at least a battery, resistor/rheostat, key, ammeter and voltmeter. Mark the components that are not connected in proper order and correct the circuit and also the circuit diagram.
SECTION-B Experiments
- To find the value of v for different values of u in case of a concave mirror and to find the focal length.
- To find the focal length of a convex mirror, using a convex lens.
- To find the focal length of a convex lens by plotting graphs between u and v or between 1/u and 1/v.
- To find the focal length of a concave lens, using a convex lens.
- To determine angle of minimum deviation for a given prism by plotting a graphbetween angle of incidence and angle of deviation.
- To determine refractive index of a glass slab using a travelling microscope.
- To find the refractive index of a liquid using convex lens and plane mirror.
- To find the refractive index of a liquid using a concave mirror and a plane mirror.
- To draw the I-V characteristic curve for a p-n junction diode in forward and reverse bias.
Activities
- To identify a diode, an LED, a resistor and a capacitor from a mixed collection of such items.
- Use of multimeter to see the unidirectional flow of current in case of a diode and an LED
- and check whether a given electronic component (e.g., diode) is in working order.
- To study effect of intensity of light (by varying distance of the source) on an LDR.
- To observe refraction and lateral deviation of a beam of light incident obliquely on a glass slab.
- To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit.
- To study the nature and size of the image formed by a (i) convex lens, or (ii) concave mirror, on a screen by using a candle and a screen (for different distances of the candle from the lens/mirror).
- To obtain a lens combination with the specified focal length by using two lenses from the given set of lenses.
Suggested Investigatory Projects
- To study various factors on which the internal resistance/EMF of a cell depends.
- To study the variations in current flowing in a circuit containing an LDR because of a variation in (a) the power of the incandescent lamp, used to ‘illuminate’ the LDR (keeping all the lamps at a fixed distance). (b) the distance of a incandescent lamp (of fixed power) used to ‘illuminate’ the LDR.
- To find the refractive indices of (a) water (b) oil (transparent) using a plane mirror, an equiconvex lens (made from a glass of known refractive index) and an adjustable object needle.
- To investigate the relation between the ratio of (i) output and input voltage and (ii) number of turns in the secondary coil and primary coil of a self-designed transformer.
- To investigate the dependence of the angle of deviation on the angle of incidence using a hollow prism filled one by one, with different transparent fluids.
- To estimate the charge induced on each one of the two identical Styrofoam (or pith) balls suspended in a vertical plane by making use of Coulomb’s law.
- To study the factor on which the self-inductance of a coil depends by observing the effect of this coil, when put in series with a resistor/(bulb) in a circuit fed up by an AC source of adjustable frequency.
- To study the earth’s magnetic field using a compass needle -bar magnet by plotting magnetic field lines and tangent galvanometer.
UK XII Physics Exam Pattern Structure
The Physics exam will be divided into a theoretical paper of 70 marks and a practical examination of 30 marks. The theoretical portion will include a variety of question types, such as multiple-choice, short answer, and long answer questions, covering all the essential units in the syllabus.
This well-curated syllabus aims to develop a strong conceptual foundation in Physics, fostering problem-solving skills and analytical thinking among students. By engaging with both theory and practical work, students will be well-prepared for further studies in science and engineering fields.
More UK Board Class 12 Syllabus Links
| Subject Name (12th) | Subject Code | Syllabus Link |
| 12th Maths | 128 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Physics | 129 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Chemistry | 130 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Biology | 131 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Hindi | 101 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th English | 103 | CLICK HERE |
| Latest UBSE Updates | UBSE | CLICK HERE |
| UK Board Class 12th All Subjects Syllabus |
All Subjects | CLICK HERE |
| Official Website | UK Board | CLICK HERE |
Related Frequently Asked Questions
How is the UK Board Class 12 Physics exam structured?
The Physics exam consists of two parts: a theory exam worth 70 marks and a practical exam worth 30 marks. The theory paper includes objective-type questions, short-answer questions, and long-answer questions.
What is the weightage of the practical exam in the Physics syllabus?
The practical exam carries a weightage of 30 marks. It includes experiments, a project report, and a laboratory record.
Are there any changes in the Physics syllabus for the academic year 2024-2025?
As of the latest update, there have been no significant changes to the syllabus. 2024-2025 syllabus remains the same.
How can students effectively prepare for the UK Board Class 12 Physics exam?
Students should focus on understanding the concepts, regularly practice numerical problems, participate in laboratory activities, and solve previous years' question papers to excel in the exam.