UKPSC has released examination scheme and syllabus for Uttarakhand Combined State Lower Subordinate Services Exam 2024-2025. UKPSC conducts Lower PCS (Provincial Civil Services) exam, aiming to recruit qualified candidates for various administrative posts across the state.
For the 2024-2025 cycle, UKPSC has updated the syllabus and exam pattern and article outlines the latest syllabus, providing insights into the updated exam pattern, key sections, and marking scheme, helping candidates to prepare effectively for their exam.
Contents
- 1 UKPSC Lower PCS Exam Pattern/Scheme 2024-2025
- 2 Preliminary Examination Pattern
- 3 Main Examination Scheme
- 4 Personal Interview
- 5 UKPSC Lower PCS Prelims Syllabus 2024-2025
- 6 Main Examination Syllabus Paper-1 General Hindi
- 7 Mains Syllabus Paper-2 Essay Writing
- 8 Mains Syllabus Paper-3 General Studies-I
- 9 Mains Syllabus Paper-4 General Studies-II
- 10 Important Links
UKPSC Lower PCS Exam Pattern/Scheme 2024-2025
The UKPSC Lower PCS Examination is conducted in three stages:
- Preliminary Examination (Prelims)
- Main Examination (Mains)
- Personal Interview
Preliminary Examination Pattern
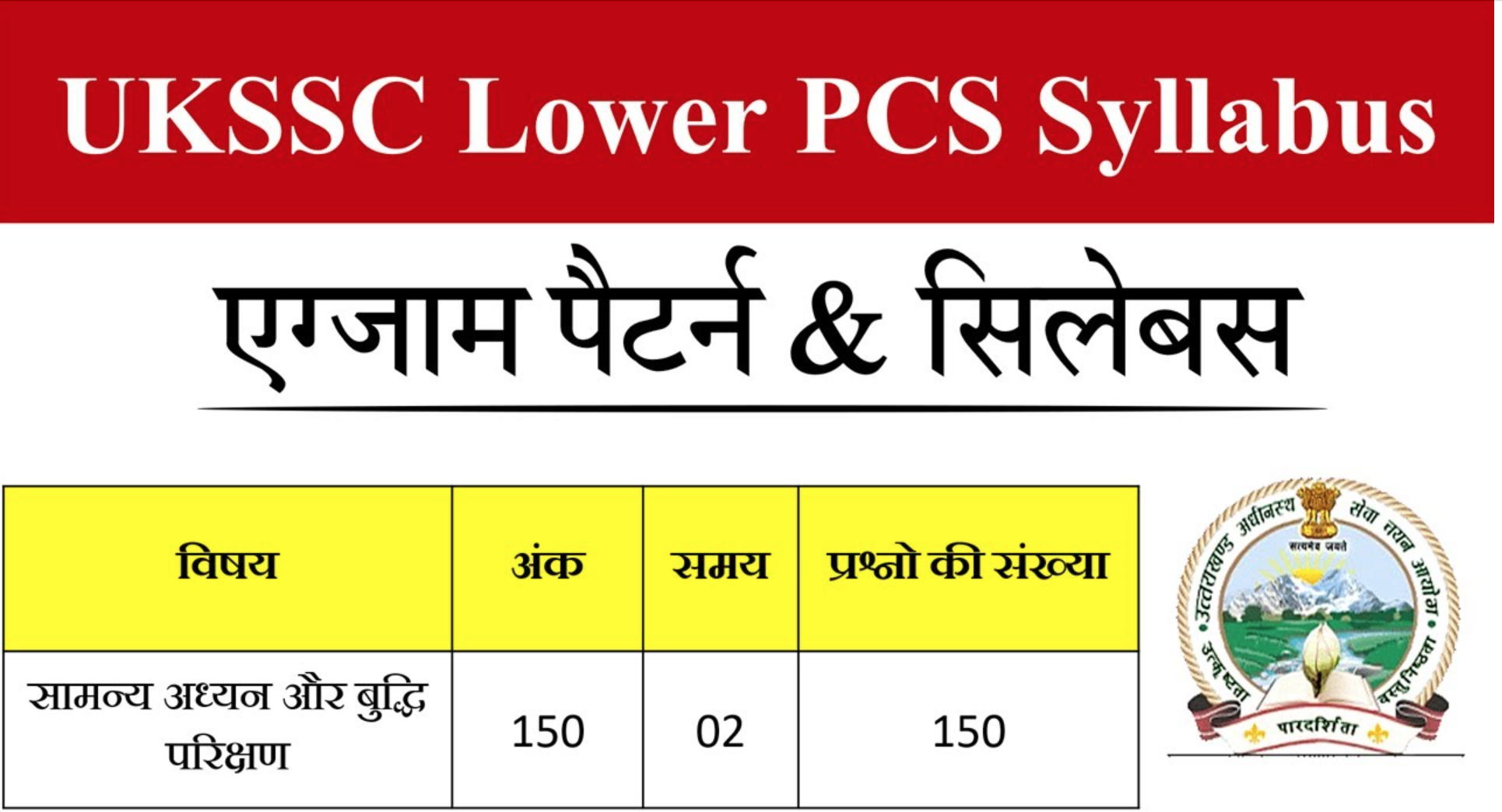
The preliminary examination is objective-based and serves as a screening test. Only candidates who qualify for this stage can proceed to the Mains examination. Key details of the Prelims are as follows:
- Mode: Offline (OMR-Based)
- Type: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Number of Papers: 1
- Total Marks: 150
- Duration: 2 hours
- Marking Scheme: +1 for each correct answer, -0.25 for each incorrect answer
Prelims Paper Structure:
| Subject | Marks | Questions |
|---|---|---|
| General Studies & Intelligence | 150 | 150 |
Main Examination Scheme
The Mains Examination is descriptive and designed to evaluate candidates comprehensive knowledge and writing ability. It consists of four papers, as detailed below:
| Paper | Marks | Ques | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paper 1: Language (General Hindi) | 100 | 06 | 02 Hours |
| Paper 2: Essay | 100 | 02 | 02 Hours |
| Paper 3: General Study : First Paper | 200 | 20 | 03 Hours |
| Paper 4: General Study : Second Paper | 200 | 20 | 03 Hours |
| INTERVIEW | 75 |
Personal Interview
The final stage is a personal interview, which assesses candidates personality, communication skills, and suitability for various administrative roles. This stage is worth 75 marks.
UKPSC Lower PCS Prelims Syllabus 2024-2025
खण्ड-1 सामान्य अध्ययन
- सामान्य विज्ञान
- भारत का इतिहास
- भारतीय राष्ट्रीय आन्दोलन
- भारतीय राज्य तंत्र, अर्थ व्यवस्था एवं संस्कृति
- भारतीय कृषि, वाणिज्य एवं व्यापार
- जनसंख्या, पर्यावरण एवं नगरीकरण (भारतीय परिप्रेक्ष्य में)
- विश्व भूगोल तथा भारत का भूगोल और प्राकृतिक संसाधन
- अधुनातन राष्ट्रीय तथा अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय महत्वपूर्ण घटनाक्रम
- उत्तराखण्ड की शिक्षा संस्कृति, कृषि, उद्योग, व्यापार एवं रहन-सहन, भौगोलिक, राजनैतिक पृष्ठ भूमि एवं सामाजिक प्रथाओं के सम्बन्ध में विशिष्ट जानकारी
- उत्तराखण्ड की सांस्कृतिक, आर्थिक व प्राकृतिक संसाधन तथा ऐतिहासिक पृष्ठ भूमि ।
खण्ड-2 सामान्य बुद्धि परीक्षण
इसके अन्तर्गत प्रश्न सामान्य बुद्धिमता से संबंधित जैसे शाब्दिक और गैर-शाब्दिक दोनों प्रकार के प्रश्न होंगे और इसमें सादृश्यों, समानताओं तथा अंतरों, स्थानिक कल्पना, समस्या, समाधान, विश्लेषण, निर्णय लेना, दृश्य स्मृति, विभेद, अवलोकन, संबंध अवधारणा, अंकगणितीय तर्क, शाब्दिक एवं चित्रात्मक वर्गीकरण, अंकगणितीय संख्या श्रृंखला आदि सम्मिलित होंगे। इसमें अभ्यर्थी की योग्यता का सामान्य विचार और संकेत और उनके संबंध, अंकगणितीय गणना तथा अन्य विश्लेषणात्मक कार्य आदि के प्रश्न भी शामिल होंगे।
Main Examination Syllabus Paper-1 General Hindi
सामान्य हिन्दी अधिकतम 100 अंक समयावधि 2 घंटे
1: वर्ण एवं शब्द:- स्वर एवं व्यंजन वर्ण, सन्धि एवं भेद, समास एवं भेद, उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय, व्याकरणिक कोटियाँ—(संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, विशेषण, क्रिया, क्रिया विशेषण तथा अव्यय) अंक:-10
2: शब्द रचना और अर्थ: पर्यायवाची शब्द, विलोम अथवा विपरीतार्थक शब्द, शब्द-युग्म, (समोच्चरितप्राय भिन्नार्थक शब्द) वाक्य या वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द, तत्सम तद्भव, देशज, विदेशी, रूढ़, यौगिक तथा योगरूढ़ शब्द अंक:-15
3: वाक्य रचना: वाक्य की परिभाषा, वाक्य के मुख्य अवयव, वाक्य और उपवाक्य, वाक्य के भेद (अर्थ एंव रचनागत) वाक्यांतरण, शब्द एवं वाक्य शुद्धिकरण, लोकोक्तियाँ एवं मुहावरे (अर्थ एवं प्रयोग) अंक:-10
4: अपठित या पाठवोधन: अपठित गद्यांश पर आधारित भाषाबोध एवं व्याकरण विषयक पाँच प्रश्न. अंक: 5×3=15
5: संक्षेपण: शीर्षक, सारांश एवं रेखांकित अंश की व्याख्या
शीर्षक-3 अंक
सारांश-6 अंक
रेखांकित की व्याख्या – 6 अंक
अंक:-15
6: हिन्दी आलेखन:
(क) सरकारी पत्र, अर्धसरकारी पत्र, परिपत्र, अनुस्मारक ( स्मरण पत्र) कार्यालय–आदेश, कार्यालय-ज्ञापन, अधिसूचना, रिपोर्ट या प्रतिविदेन ।
(ख) अंग्रेजी-गद्यांश का हिन्दी अनुवाद
हिन्दी-गद्यांश का अंग्रेजी अनुवाद
अंक: – 10 +10 = 20
Mains Syllabus Paper-2 Essay Writing
निबंध अधिकतम अंकः 100 समयः 2 घंटे: इस प्रश्नपत्र में दो खण्ड ‘अ’ और ‘ब’ होंगे। प्रत्येक खण्ड से निम्नलिखित में से किसी एक विषय पर लगभग 700 शब्दों का निबंध लिखना होगा :
खण्ड-अ
- साहित्य एवं संस्कृति ।
- सामाजिक, राजनीतिक और आर्थिक |
- राष्ट्रीय / अंतर्राष्ट्रीय विषय ।
- राष्ट्रीय विकास, विज्ञान एवं प्रौद्योगिकी से संबंधित नीतियाँ ।
- पर्यावरण एवं प्राकृतिक आपदा ( भू-स्खलन, जलप्रलय, सूखा एवं भूकंप आदि )
खण्ड–ब
- उत्तराखंड का ऐतिहासिक, कलात्मक एवं सांस्कृतिक परिदृश्य ।
- उत्तराखंड की सामाजिक एवं सांस्कृतिक संरचना ।
- उत्तराखंड में पर्यावरण संरक्षण एवं आपदा प्रबंधन ।
- उत्तराखंड में महिलाओं की आर्थिक एवं राजनैतिक भूमिका तथा महिला सशक्तिकरण ।
- उत्तराखंड का आर्थिक एवं भौगोलिक परिदृश्य एवं पर्यटन | उत्तराखंड में पलायन की समस्या ।
Mains Syllabus Paper-3 General Studies-I
HISTORY, ART, CULTURE AND SOCIETY OF INDIA
- Various Art forms, from Ancient to Modern period- their important elements. Literature, Painting, Music.
- Bhakti Movement, Sufism, its impact on Indian culture. Main personalities.
- Social-religious Movements and their impact on people and their life. Indian Architecture – Main monuments, their chief characteristics. Ancient Indian history-important rulers and their contribution.
- Medieval India-Important rulers, their policies, and transition to modern India (various reasons for the decline of Muslim rule, situation of turmoil and transition to modern India)
- Modern India-
• Power struggle between foreign powers in India, rise of the British in India, their policies and its impact on India and the Indians, major British rulers.
• Impact of British economic policies.
• Drain of Wealth (From India)
• Establishment of railways and other means of communication, did these services serve British economic interests.
• Progress of education, English approach towards Indian education policy.
• British policy towards Afghanistan, Burma, Tibet. Its impact on India and
the world.
• British relations with native Indian rulers.
• Policies like Subsidiary Alliance, Doctrine of Lapse, Objectives of the - British and their later effects.
Freedom movement
• Renaissance in India and its impact on the national movement.
• Mahatma Gandhi’s debut on the national stage.
• Various dimensions of the national movement – from Non-cooperation movement to Cabinet mission.
• Participation of Masses from different parts of India.
• Farmers and tribal movements which gave impetus to the national movement.
• The ideology of the prominent personalities who provided the base to the national movement.
• Partition-Condition and Causes. - Challenges before India after Independence
• Economic challenges.
• Building the nation through social and cultural initiative.
• Implementation of Five-year plan and later establishment of NITI Aayog.
History, Arts, Culture and Society of Uttarakhand
History of Uttarakhand : Pre historic and Proto- historic background ( stone age tools, The Painted Grey Ware culture, Megalithic cultures), Excavated Archaeological sites, Sources for the history of Cultural Pasts of Utttarkhand (Literary, Archaeological, Oral), Ancient Tribals and Communities, Kunindas and Yaudheyas, Administration and Cultural contributions of Katyuri, Parmar and Chand dynasty. Relations of the rulers of Uttarakhand with Sikhs, Rulers of Delhi, Nepal and Sirmor in Medieval times, Invasion of Gorkhas and its impact, Administration and Slave trade, Advent of European travelers, surveyors and missionaries, Establishment of Army Cantonments and its social impact, Colonial land and land revenue administration, Forestry, Excise Policy, Regional Political Organizations, Press and Journalism, Arya Samaj and Shuddhikaran movement, Popular People’s protest- Coolie Begar, Dola-Palki, Gadi-Sadak, Forest Agitations, Arrival of Gandhi in Uttarakhand (1915, 1929) and Mass mobilization, Local responses to the Gandhian movements and popular participation, Indian National Army and its support base, Tehri Riyasat; Administration, Dhandhak, Prajamandal movement and merger into Indian Union, Struggles for the formation of separate state in Uttarakhand.
Religious life and Cults (Shaivism, Vaishanvism, Buddhism, Jainism, Nath Cult, Lakulish), Temple Architecture- Types and Features, Rock Art, Metallic Art, Wooden Art, Tradtional Knowledge System and architecture, Paintings, Music, Dance and Songs, Hydraulic Architecture- Kup, Naula, Khal, Gharat, Folk deity, Jagar, Pandav Lila, Dress, Costumes and Ornaments, Fairs and Festivals, Pilgrimage and Tourist spots-Hemkund Sahib, Nanak Matta, Kailash Mansarovar, Piran Kaliyar, Kumbh Fair, Char Dham Yatra, Nanda Raj Jat Yatra, Folk musical instruments, Food habits and local cuisines, Important personalities of Uttarakhand (Spiritual Saints, Freedom fighters, Authors, Artists), Garhwali and Kumauni language and literature, Government measures of conservation of Language and Culture.
INDIAN CONSTITUTION, POLITICAL SYSTEM AND ADMINISTRATIVE SYSTEM
- Evolution of Indian Constitution: History and Constituent Assembly Debates; Salient features; Preamble and Basic Structures; Amendment Procedures and Amendment Acts.
- Rights and Duties: Citizenship; Fundamental Rights; Directive Principles of State Policy; Relationship between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy; and Fundamental Duties.
- Union and State Executive: President; Prime Minister and Council of Ministers- Power and Functions; Governor; Chief Minister and Council of Ministers- Power and Functions.
- Union and State Legislatures: Indian Parliament-Powers and Functions; State Legislatures-Powers and Functions.
- Indian Judiciary: Supreme Court-Composition, Powers and Functions; High Courts- Composition, Powers and Functions; Judicial Review; and Judicial Activism.
- Elections and Political Parties in India: National and State Parties; Election Commission of India; Electoral laws; Model Code of Conduct; Anti-Defection Laws; and Electoral Reform Measures.
- Indian Federal Structure: Central-State Relations- Legislative, Financial and Administrative; Panchayati Raj and Municipal Institutions.
- Constitutional Bodies and Administrative Control Mechanisms: Constitutional Functionaries; Constitutional, Legislative and Judicial Control over Administration.
- Administrative System and Administrative Reforms: NITI Aayog; Different Tribunals; E-Governance; Lokpal; Right to Information (RTI); Right to Education (RTE); Right to Public Services; Citizen Charters; Role of Ministries and Departments; Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) Recommendations.
- National Integration and Challenges: Insurgency; Internal Security; Inter-State Disputes.
POLITICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE SYSTEM OF UTTARAKHAND
- Political and Administrative System of Uttarakhand: Structure and Processes.
- Legislative Assembly in Uttarakhand: Powers and Functions.
- Judiciary in Uttarakhand: Appointment of High Court and Lower Court Judges; Powers and
- Functions; Lok Adalat; Lokayukta; Uttarakhand Public Services Tribunal and Judicial Interventions.
- Political Parties in Uttarakhand: Elections, Leadership, Anti-Defection Law, Political Participation and Accountability.
- Local Self-Government in Uttarakhand: Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and Urban Local Bodies; Role of State Election Commission.
- Social Issues and Contemporary Problems in Uttarakhand: Leadership Issues; Problem of Corruption; Role of Civil Society & Media; Anti-Alcohol Movement, Problems of Minorities’; Women and Weaker Sections in Uttarakhand; Climate Change; Power Projects and threat of Lake and Cloud Burst; Illegal Mining; Human-Animal Conflict; Human
- Political and Trafficking and Drug Abuse Menace.
- Administrative Services and Control in Uttarakhand: The Uttarakhand Right to Service Act, 2011; Social Audit; Citizen Charter; Vigilance Establishment Uttarakhand.
- Social Schemes/Programmes in Uttarakhand: Women and Child; Health and Wellness; Education and Learning; Business and Entrepreneurship; Agriculture, Rural and Environment; Banking, Financial Services and Insurance; Housing and Shelter; Skills and Employment; Sports and Culture.
- National Basic Services Schemes/Programmes in Uttarakhand: National Health Mission; Uttarakhand Renewable Energy Development Agency (UREDA); Uttarakhand State Rural Livelihoods Mission; Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme; Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali Paryatan Swarozgar Yojana; Rural Enterprise Acceleration Project (REAP); Uttarakhand Skill Development Mission, 2013 (UKSDM); Deen Dayal Upadhyay Grah Aawas (Home Stay) Scheme.
- Government Initiatives for Social Inclusion: The Uttarakhand Public Services (Reservation for Economically Weaker Sections) Act, 2019; The Uttarakhand Public Services (Horizontal Reservation for Women) Act, 2022;
- 10 per cent Reservation in government jobs for statehood activists and their dependents and Acts related to marginalized and other socially/economically
weaker sections; State Uniform Civil Code.
General Science, Technology and Environment
- Questions on General Science, Technology and Environment shall be such that they shall cover general understanding and application of Science, Technology and Environment including matters of day-to-day observation and experience, as may be expected from an educated person who has not made a special study of any particular branch of science, technology and environment.
- Worldwide environmental issues (like air pollution, atmospheric pollution and water pollution) and solutions for control on them, green house effect and global warming, ozone depletion in stratosphere, forest degradation, deforestation and carbon absorption.
- Principles of biotechnology, Use of biotechnology for improvement of living standards in the field of human health and food production.
- Infectious life style of human beings and its prevention. Nutritional requirements for human growth, Diseases of animals, birds and plants and their prevention.
- Polymers (biopolymers and bio plastics) and solution. Fundamental environmental chemistry, Soil pollution and their treatment. Origin of life, Biological evolution and chemical toxicology, Principles of green chemistry and their products, Genetic disorder.
- General idea of Force, Energy, Light, Electricity, Magnetism, Semiconductor, Nuclear Energy, Astrophysics and their uses in daily life.
- Basics of computers, it’s components and it’s applications in daily life. Basics of information technology, it’s applications and it’s impact on daily life. Uses of word-processing, spreadsheet and presentation software. Uses of internet and email. Cyber crime and basics of cyber laws, Basics of e- Governance and it’s applications, e-Governance related aspects in Uttarakhand.
Human Values, Work Culture and Civil Service Aptitude
- Human Values: Nature and Types, Importance and Characteristics
- Role of Family, Society and Education in inculcating Human Values.
- Work Culture: Concept, Approaches to Work Culture; Work Culture for Effective Performance, Role of Work Culture in Administration.
- Attitude: Concept, Structure and Functions and its Application in Governance.
- Aptitude: Meaning, Role of Aptitude and Foundational Values in Public Services- Integrity, Impartiality, Objectivity, Empathy and Dedication.
- Emotional Intelligence: Concept and Application in Administration and Governance.
- Public/Civil services: Values and Ethics in Public Administration Concerns and Dilemmas in Government and Private Institutions, Ethical Issues in Public Organisations.
- Probity in Governance: Meaning, Features, Deficit in Ethical and Moral Values in Governance. Information Sharing and Transparency in Government.
- Contribution of Indian Moral Thinkers and Philosophers: Mahatma Gandhi, B.R. Ambedkar, Swami Vivekanand, Rabindra Nath Tagore, and APJ Abdul Kalam.
- Case Studies on Above Topics.
Mains Syllabus Paper-4 General Studies-II
INDIAN ECONOMY
- Basic Features of Indian economy, National income and per capita income: Meaning & trends, Sectoral composition and structural changes, Problems of sustainable development. Human Development index. Inclusive growth: issues and policy initiatives, Economic empowerment of women.
- Economic Planning in India: Objectives, strategy, achievements & limitations, Rational, objectives and functions of NITI Aayog. Regional imbalances, Poverty, Economic Inequality, Inflation and unemployment: Meaning, causes, effects & Policy initiatives.
- Trends of agricultural production, productivity and prices, commercialization and diversification, Institutional and technological Changes, Agricultural Price Policy, Rural credit: Issues, Progress & Policy initiatives, Food security: Meaning, Issues, Progress & Policy initiatives, Farm subsidy: Issues, Problems, effects & Policy Initiatives, Industrial Production in India: Trends & composition, Industrial Policy and its effects on growth, Role of MSMEs, Disinvestment: Challenges and Policy.
- Tax Structure in India, Goods and Service Tax (GST) : Concept, features, progress & limitation, Fiscal federalism, Fiscal Policy and reforms, Main features of Current Union Budget, Black economy : Meaning, Issues, Estimates & Policy initiatives, Trend, Direction and composition of India’s foreign trade, Reforms in India’s external sector, India’s BOP Performance and Policy, India and Economic International institutions, organizations and groups, Public Debt : Issues & Management, Financial sector reforms in India, Digital Payments: Issues, Methods, Effects & Policy initiatives, Inclusive finance, Monetary Policy of RBI.
- Broad demographic features of India, Migration and economic development, Issues related to urbanisation, Infrastructure sector in India: Growth drivers and Policy initiatives.
ECONOMY OF UTTARAKHAND
- Features of Uttarakhand Economy, State GDP and Per Capita Income, Structural Changes, Natural and Human Resources, Population and Demography, Forest, Energy, Agriculture and Animal wealth. Water Resources and Energy Development, Natural Disasters, Herbs and Minerals.
- Trade, Commerce and Industry: Inter-state trade, Manufacturing, Heavy, Medium, Small Scale and Cottage Industries development. Transport – Roads, Railways, Airports: Programmes and Challenges.
- Public Finance: Budget, Fiscal Policy and Fiscal Reforms, Taxes and Taxation, Public Income and Financial Deficit, Public Expenditure and Debt.
- Human Development: Human Development Index, Literacy and Education System, Poverty and Poverty Alleviation Programmes, Unemployment and Employment Schemes/Programs, Health and Sanitation, Pension and Insurance, Social Welfare and Government Schemes, Displacenment and Migration, Economic Empowerment of Women.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: Major Crops, Fruit Production, Animal Husbandry, Agricultural Holdings and Land Reforms, Farmer Welfare, Panchayati Raj, Community Development and Cooperative Movement, Technological Changes, Agricultural Marketing, Minimum Support Price, Rural Development Scheme.
- Banking and Finance: Present Scenario, Development of Banking and Its Contribution to State GDP, Inclusive Finance, Rural Credit – Challenges and Policy.
- Tourism and Pilgrimage: Contribution of Tourism and Pilgrimage in Economic Development, Eonomic Importance of Religious Tourism, Tourism Development Programmes and Plans.
Geography of India and Demography
It will include question on broad understanding of Indian Geography and Demography. Questions will be asked on the following topics:
• Physical features of India.
• Geological System and Structure.
• Relief, Drainage and Interlinking of Rivers.
• Climate phenomena: El-Nino, La-Nina, Southern Oscillation, Western Disturbances, Consequences of Climate Change.
• Soils degradation and Deforestation.
• Forest, Forest products, Wildlife Sanctuaries, National Parks, Biodiversity Hot-Spot.
• Environmental problems and Ecological Issues in India.
• International boundaries of India and related Geopolitical Issues.
• Salient features of Indian Agriculture, Agro-based activates, Land Reforms, Problems of Wasteland and their reclamation.
• Mines and Minerals, Energy resources, Energy crisis and search for alternatives.
• Industrial development in India.
• Major Transport Corridors, Problems and prospects of Civil Aviation and Water Transport.
• Regional disparities in Economic Development of India.
• Natural Hazards and Disasters in India.
• Regional consciousness and Nation integration of India on the basis of Physical and Demographic characteristics, Geographical basis of Center-State relations.
• Distribution and growth of population in India, Demographic characteristics, Dependency Ratio, Migration (Interregional, Interstate and International).
GEOGRAPHY OF UTTARAKHAND, DEMOGRAPHY AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT
• Geographical set up and geo-political significance of Uttarakhand.
• Origin of Uttarakhand Himalaya, physiographic divisions of Uttarakhand and geographical conditions responsible for the inhabitation in different physiographic divisions.
• Major rivers, their origin and significance-geographical, economic, cultural, environmental and religious.
• Major mountains and their significance- geographical, economic, cultural, environmental and religious.
• Climate including causes and effects of climatic diversity.
• Forest resources and the factors affecting different forest types, forest diversity and physiography; altitudinal zones and climatic conditions, forest resources and economic development, conservation of forest resources.
• Development of horticulture and responsible geographical factors and climatic variability, Challenges to horticulture.
• Major crops and geographical factors and climatic conditions responsible for crop diversity. Causes and effects of crop rotation.
• Means of irrigation and geographical factors affecting their development. Major projects of irrigation, irrigation schemes, Minor Irrigation.
• Agricultural holdings – types and their causes.
• Natural and man-made calamities and disaster management- types, causes and their impact on human life. Role of disaster management in natural and man-made calamities, Impact of natural and man-made calamities on human life and environment. Efforts of Uttarakhand Government to mitigate the impact of disasters.
• Water crisis and watershed management – factors responsible for water crisis, impact of water crisis on human life. Role of watershed management in mitigating water crisis, significance of watershed management, challenges to watershed management.
• Problems of remote areas – types and causes of environmental challenges, economic challenges, health challenges and access to basic services. Efforts of Uttarakhand Government to overcome the problems of remote areas.
• Environment and environmental movements-major environmental movements, their causes and impact upon the development of Uttarakhand.
• Biodiversity and its preservation-types of biodiversity, factors affecting biodiversity of Uttarakhand, Uttarakhand Himalaya as a Biodiversity Hot-Spot of Himalaya, relevance of biodiversity, threats to biodiversity/challenges to biodiversity, Major initiatives for conservation efforts in Uttarakhand.
• Population of Uttarakhand – diversity in distribution, density, sex-ratio, literacy and factors affecting them. Migration and its causes and impact of out-migration.
Statistical analysis, graph and diagram:- Statistical analysis of data through measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, graphs and diagrams along with corresponding concepts of their application.
Current events:- Current events of international and national importance alongwith games and sports related to the following:
(1) Global
(2) Asia
(3) India
(4) Uttarakhand
Important Links
- To Download UKPSC Lower PCS Syllabus 2025 PDF In Hindi/English: CLICK HERE
- Must Read: UKPSC RO ARO (Accounts) Syllabus Exam Pattern 2024 (Prelims & Mains)
- Must Read: Uttarakhand ARO RO Syllabus 2024 UKPSC Samiksha Adhikari Exam Pattern [Advocate Gen. Office Nainital]
- Also Read: UKPSC Review Officer (RO) Syllabus 2024 (Uttarakhand State Election Commission)
- Also See: Uttarakhand UKPSC Upper PCS Syllabus 2024 Prelims & Mains In Hindi PDF
- For Uttarakhand Latest Government Jobs:- https://4syllabus.in/tag/uttarakhand/
- UKPSC Official Exam Calendar 2024-2025:- UKPSC Exam Calendar 2024-2025
- Official Website: https://psc.uk.gov.in/
The UKPSC Lower PCS Exam 2024-2025 offers a pathway to meaningful administrative roles within Uttarakhand. A clear understanding of the updated syllabus and exam pattern, along with a disciplined preparation strategy, will be crucial in achieving success.







