Uttarakhand Board of School Education (UBSE) has released the Physics syllabus for Class 11th (eleventh) for the academic session 2024-2025. The syllabus is designed to help students grasp fundamental concepts in physics, preparing them for higher education and competitive exams.

Contents
UK Board Class 11th Physics Syllabus Overview
The Class 11 Physics syllabus is divided into two main parts:-
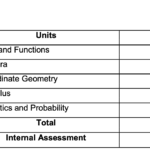
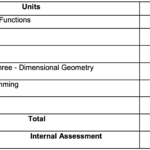
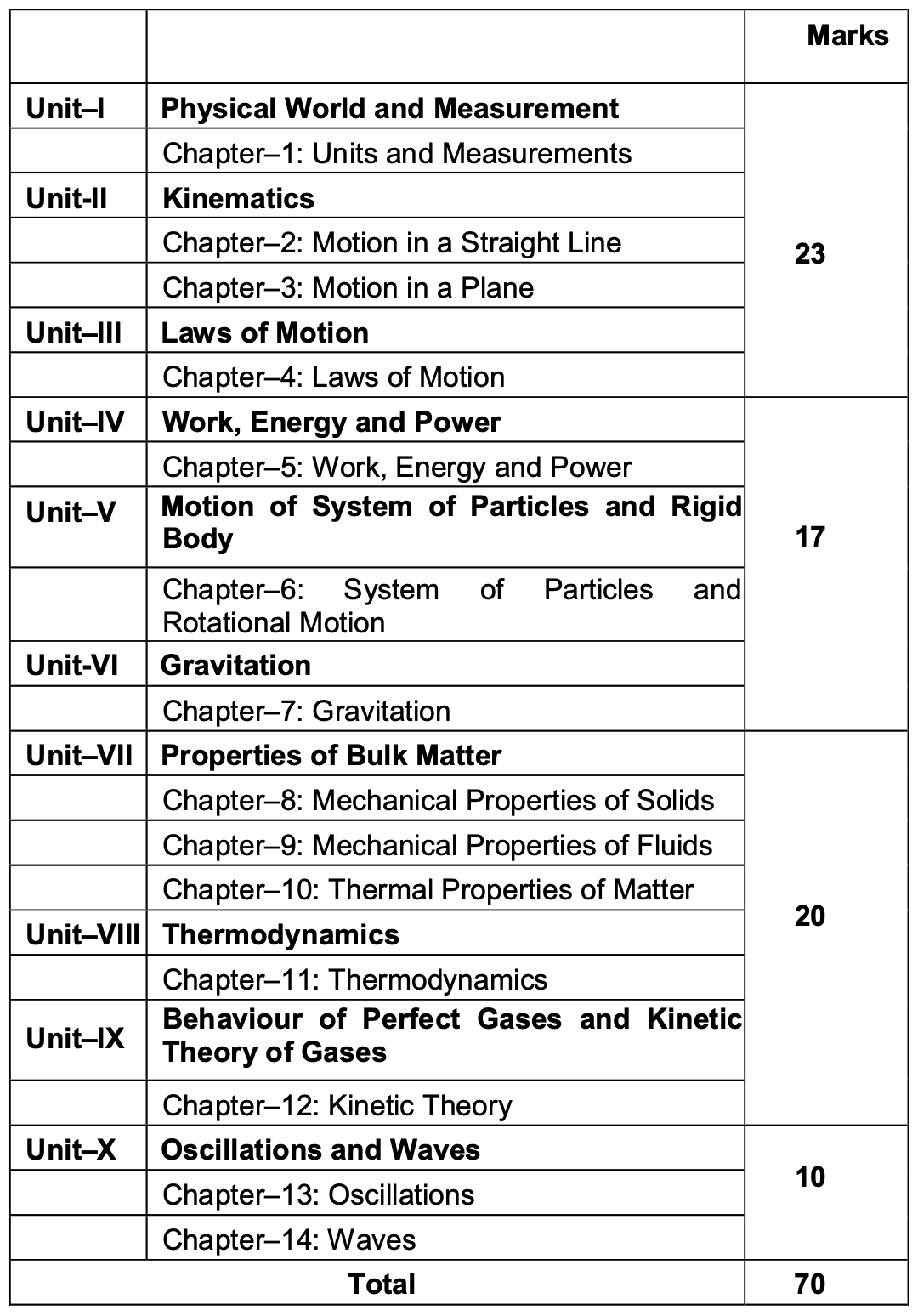
Theory (70 Marks): This section covers a wide range of topics that are crucial for a deep understanding of physics. The syllabus is structured into the following units:
Unit I : Physical World and Measurement
Chapter–1: Units and Measurements: Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental and derived units. significant figures. Dimensions of physical quantities, dimensional analysis and its applications.
Unit II : Kinematics
Chapter–2: Motion in a Straight Line : Frame of reference, Motion in a straight line, Elementary concepts of differentiation and integration for describing motion, uniform and non- uniform motion, and instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, velocity – time and position-time graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated motion (graphical treatment).
Chapter–3: Motion in a Plane: Scalar and vector quantities; position and displacement vectors, general vectors and their notations; equality of vectors, multiplication of vectors by a real number; addition and subtraction of vectors, Unit vector; resolution of a vector in a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and Vector product of vectors.
Motion in a plane, cases of uniform velocity and uniform acceleration- projectile motion, uniform circular motion.
Unit : III Laws of Motion
Chapter–4: Laws of Motion: Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton’s first law of motion; momentum and Newton’s second law of motion; impulse; Newton’s third law of motion.
Law of conservation of linear momentum and its applications.
Equilibrium of concurrent forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of friction, rolling friction, lubrication.
Dynamics of uniform circular motion: Centripetal force, examples of circular motion (vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a banked road).
Unit : IV Work, Energy and Power
Chapter–5: Work, Energy and Power: Work done by a constant force and a variable force; kinetic energy, work- energy theorem, power.
Notion of potential energy, potential energy of a spring, conservative forces: non-conservative forces, motion in a vertical circle; elastic and inelastic collisions in one and two dimensions.
Unit : V Motion of System of Particles and Rigid Body
Chapter–6: System of Particles and Rotational Motion: Centre of mass of a two-particle system, momentum conservation and
Centre of mass motion. Centre of mass of a rigid body; centre of mass of a uniform rod.
Moment of a force, torque, angular momentum, law of conservation
of angular momentum and its applications.
Equilibrium of rigid bodies, rigid body rotation and equations of rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational motions.
Moment of inertia, radius of gyration, values of moments of inertia for simple geometrical objects (no derivation).
Unit : VI Gravitation
Chapter–7: Gravitation: Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity and its variation with altitude and depth.
Gravitational potential energy and gravitational potential, escape speed, orbital velocity of a satellite.
Unit : VII Properties of Bulk Matter
Chapter–8: Mechanical Properties of Solids: Elasticity, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke’s law, Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, shear modulus of rigidity (qualitative idea only), Poisson’s ratio; elastic energy.
Chapter–9: Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal’s law and its applications (hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid pressure.
Viscosity, Stokes’ law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, critical velocity, Bernoulli’s theorem and its simple applications.
Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise.
Chapter–10: Thermal Properties of Matter: Heat, temperature, thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases, anomalous expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv – calorimetry; change of state – latent heat capacity.
Heat transfer-conduction, convection and radiation, thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wein’s displacement Law, Stefan’s law .
Unit VIII : Thermodynamics
Chapter–11: Thermodynamics: Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature, zeroth law of thermodynamics, heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics,
Second law of thermodynamics: gaseous state of matter, change of condition of gaseous state -isothermal, adiabatic, reversible, irreversible, and cyclic processes.
Unit IX : Behaviour of Perfect Gases and Kinetic Theory of Gases
Chapter–12: Kinetic Theory: Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done in compressing a gas.
Kinetic theory of gases – assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature; rms speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of equi-partition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro’s number.
Unit : X Oscillations and Waves
Chapter–13: Oscillations: Periodic motion – time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time, periodic functions and their applications.
Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) and its equations of motion; phase; oscillations of a loaded spring- restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M.
Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum derivation of expression for its time period.
Chapter–14: Waves: Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal waves, speed of travelling wave, displacement relation for a progressive wave, principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats.
UK Board Physics 11th Practical Syllabus 2024-25
Practical Examination (30 Marks): Practical experiments and activities are essential for understanding the theoretical concepts. The practical syllabus includes experiments related to optics, electricity, magnetism, and more. Students are also required to submit a project report and a laboratory record.
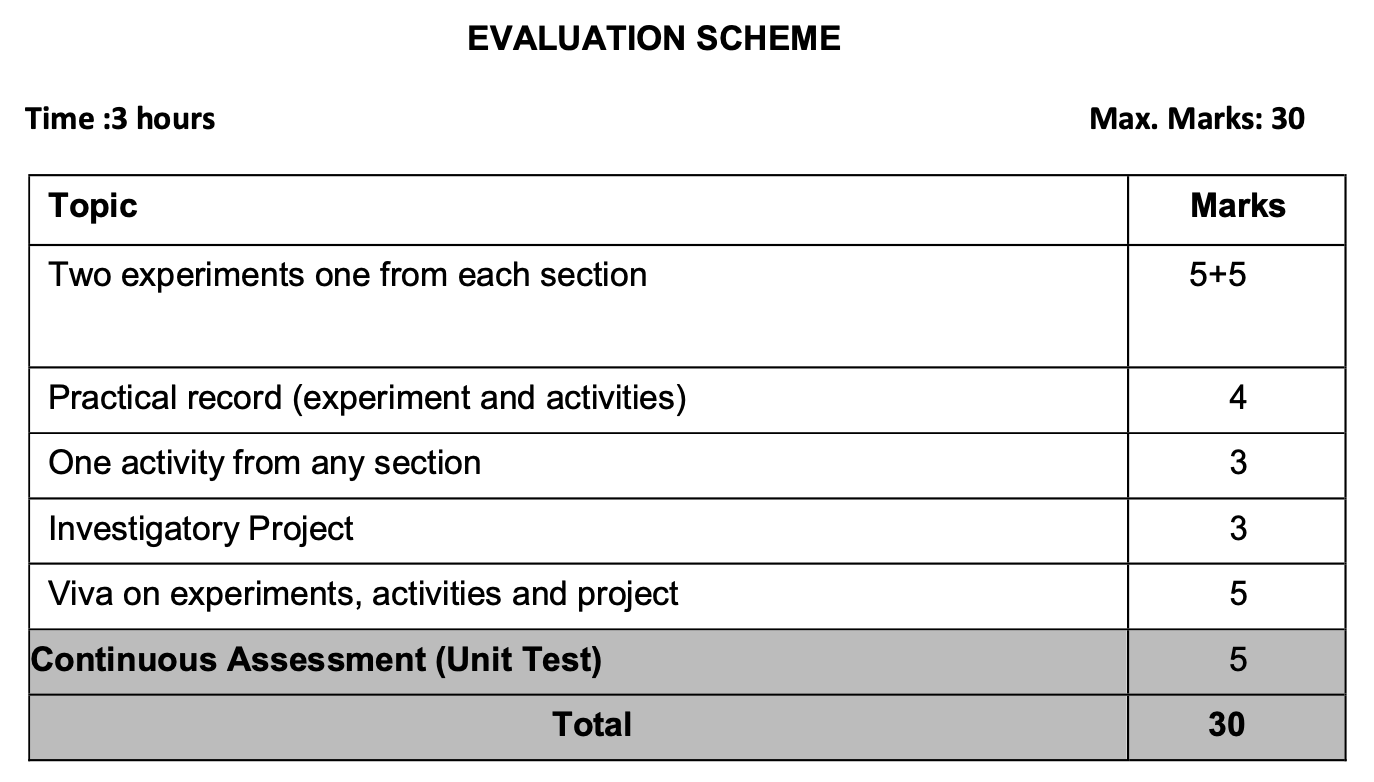
Experiments SECTION–A
- To measure diameter of a small spherical/cylindrical body and to measure internal diameter and depth of a given beaker/calorimeter using Vernier Callipers and hence find its volume.
- To measure diameter of a given wire and thickness of a given sheet using screw gauge.
- To determine volume of an irregular lamina using screw gauge.
- To determine radius of curvature of a given spherical surface by a spherometer.
- To determine the mass of two different objects using a beam balance.
- To find the weight of a given body using parallelogram law of vectors.
- Using a simple pendulum, plot its L-T graph and use it to find the effective length of second’s pendulum.
- To study variation of time period of a simple pendulum of a given length by taking bobs of same size but different masses and interpret the result.
- To study the relationship between force of limiting friction and normal reaction and to find the co- efficient of friction between a block and a horizontal surface.
- To find the downward force, along an inclined plane, acting on a roller due to gravitational pull of the earth and study its relationship with the angle of inclination θ by plotting graph between force and Sinθ.
Activities
- To make a paper scale of given least count, e.g., 0.2cm, 0.5 cm.
- To determine mass of a given body using a metre scale by principle of moments.
- To plot a graph for a given set of data, with proper choice of scales and error bars.
- To measure the force of limiting friction for rolling of a roller on a horizontal plane.
- To study the variation in range of a projectile with angle of projection.
- To study the conservation of energy of a ball rolling down on an inclined plane (using a double inclined plane).
- To study dissipation of energy of a simple pendulum by plotting a graph between square of amplitude and time.
Experiments SECTION–B
- To determine Young’s modulus of elasticity of the material of a given wire.
- To find the force constant of a helical spring by plotting a graph between load and extension.
- To study the variation in volume with pressure for a sample of air at constant temperature by plotting graphs between P and V, and between P and 1/V.
- To determine the surface tension of water by capillary rise method.
- To determine the coefficient of viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal velocity of a given spherical body.
- To study the relationship between the temperature of a hot body and time by plotting a cooling curve.
- To determine specific heat capacity of a given solid by method of mixtures.
- To study the relation between frequency and length of a given wire under constant tension using sonometer.
- To study the relation between the length of a given wire and tension for constant frequency using sonometer.
- To find the speed of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube by two resonance positions.
Activities
- To observe change of state and plot a cooling curve for molten wax.
- To observe and explain the effect of heating on a bi-metallic strip.
- To note the change in level of liquid in a container on heating and interpret the observations.
- To study the effect of detergent on surface tension of water by observing capillary rise.
- To study the factors affecting the rate of loss of heat of a liquid.
- To study the effect of load on depression of a suitably clamped metre scale loaded at (i) its end (ii) in the middle.
- To observe the decrease in pressure with increase in velocity of a fluid.
Uttarakhand Class XI Physics Examination Pattern
The Physics paper is divided into two sections: theory and practical. The theory exam is for 70 marks, while the practical exam accounts for 30 marks. The theory exam consists of objective-type questions, short-answer questions, and long-answer questions. Some Important points are:-
- Internal Assessment: Students will be assessed internally for regular attendance, assignments, and practical performance.
- Preparation Tips: To excel in the Physics exam, students should focus on understanding the concepts rather than rote learning. Regular practice of numerical problems, solving previous years’ papers, and participating in lab activities are recommended.
The UBSE Class 11 Physics syllabus for 2024-2025 is comprehensive, aiming to build a solid foundation for students aspiring to pursue higher studies in science and engineering.
More UK Board Class 11 Syllabus Links
| Subject Name (11th) | Subject Code | Syllabus Link |
| 11th Maths | 128 | CLICK HERE |
| 11th Physics | 129 | CLICK HERE |
| 11th Chemistry | 130 | CLICK HERE |
| 11th Biology | 131 | CLICK HERE |
| 11th Hindi | 101 | CLICK HERE |
| 11th English | 103 | CLICK HERE |
| Latest UBSE Updates | UBSE | CLICK HERE |
| UK Board Class 12th All Subjects Syllabus |
All Subjects | CLICK HERE |
| Official Website | UK Board | CLICK HERE |
FAQS Related To UK Board 11th Physics Syllabus
How is the Physics syllabus structured for the academic year 2024-2025?
The syllabus is divided into theoretical concepts and practical experiments. The theory part covers various chapters focusing on fundamental principles of Physics, while the practical section involves experiments that reinforce these concepts.
What is the weightage of different sections in the Class 11th Physics exam?
The exam is typically divided into two parts: a theoretical paper worth 70 marks and a practical examination worth 30 marks. The theoretical portion covers all major topics, while the practical part assesses students’ ability to conduct experiments and understand their outcomes.
How can students effectively prepare for the UK Board Class 11th Physics exam?
Students should focus on understanding the core concepts of each topic, practice numerical problems regularly, and perform the experiments outlined in the syllabus. Referring to the textbook prescribed by UBSE and practicing previous years’ question papers can also be helpful.
Are there any changes in the Physics syllabus for the academic year 2024-2025 compared to previous years?
Any changes or updates to the syllabus will be officially announced by the Uttarakhand Board of School Education. It's advisable for students and teachers to regularly check the official UBSE website or contact their schools to stay informed about any modifications.
![UK Board Class 11th Biology Syllabus 2024-2025 [XI UBSE Uttarakhand] feature image](https://4syllabus.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/UK-Board-Class-11th-Biology-Syllabus-2024-2025-XI-UBSE-Uttarakhand-feature-image-150x150.webp)