UK Board Class 12th Biology Syllabus for the 2024-2025 academic year is designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of various biological concepts, essential for building a solid foundation for higher education in the life sciences.
The syllabus is structured to cover a wide range of topics that are crucial for students aspiring to pursue careers in medicine, biotechnology, environmental science, and related fields. Check UK board class 12 biology syllabus along with detailed XII (twelfth) biology board examination pattern with list of practicals, activities and projects.

Contents
UK Board Class 12th Biology Syllabus 2024-2025
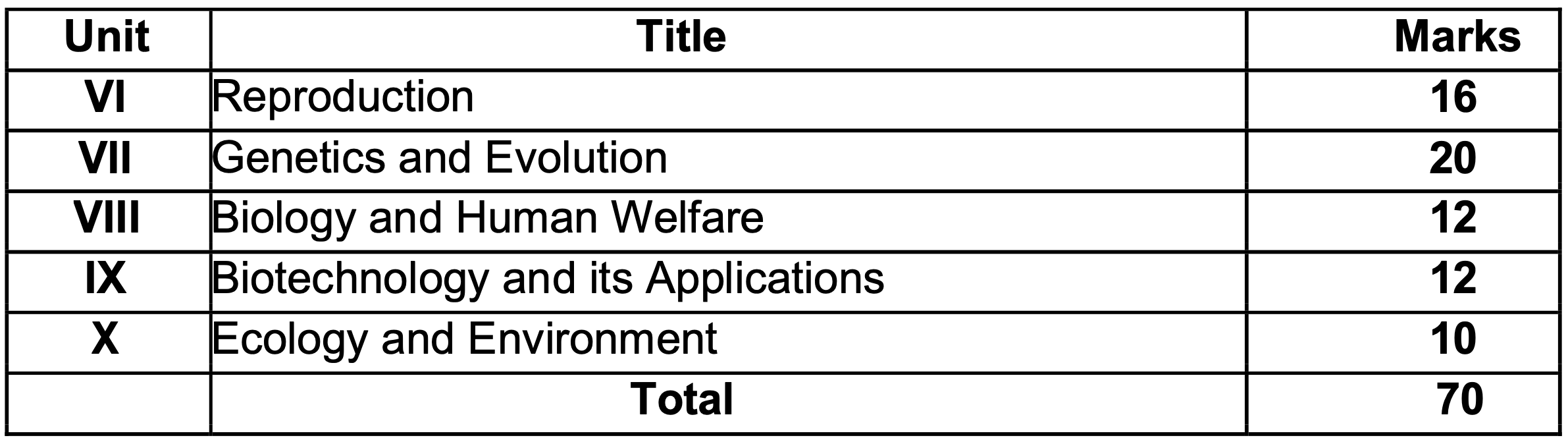
Unit-VI Reproduction
- Chapter-1: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants:- Flower structure; development of male and female gametophytes; pollination – types, agencies and examples; out breeding devices; pollen-pistil interaction; double fertilization; post fertilization events – development of endosperm and embryo, development of seed and formation of fruit; special modes- apomixis, parthenocarpy, polyembryony; Significance of seed dispersal and fruit formation.
- Chapter-2: Human Reproduction:- Male and female reproductive systems; microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary; gametogenesis -spermatogenesis and oogenesis; menstrual cycle; fertilisation, embryo development up to blastocyst formation, implantation; pregnancy and placenta formation (elementary idea); parturition (elementary idea); lactation (elementary idea).
- Chapter-3: Reproductive Health:- Need for reproductive health and prevention of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs); birth control – need and methods, contraception and medical termination of pregnancy (MTP); amniocentesis; infertility and assisted reproductive technologies – IVF, ZIFT, GIFT (elementary idea for general awareness).
Unit-VII Genetics and Evolution
- Chapter-4: Principles of Inheritance and Variation: Heredity and variation: Mendelian inheritance; deviations from Mendelism – incomplete dominance, co-dominance, multiple alleles and inheritance of blood groups, pleiotropy; elementary idea of polygenic inheritance; chromosome theory of inheritance; chromosomes and genes; Sex determination – in humans, birds and honey bee; linkage and crossing over; sex linked inheritance – haemophilia, colour blindness; Mendelian disorders in humans – thalassemia; chromosomal disorders in humans; Down’s syndrome, Turner’s and Klinefelter’s syndromes.
- Chapter-5: Molecular Basis of Inheritance:- Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material; Structure of DNA and RNA; DNA packaging; DNA replication; Central Dogma; transcription, genetic code, translation; gene expression and regulation – lac operon; Genome, Human and rice genome projects; DNA fingerprinting.
- Chapter-6: Evolution: Origin of life; biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (paleontology, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidences); Darwin’s contribution, modern synthetic theory of evolution; mechanism of evolution – variation (mutation and recombination) and natural selection with examples, types of natural selection; Gene flow and genetic drift; Hardy – Weinberg’s principle; adaptive radiation; human evolution.
Unit-VIII Biology and Human Welfare
- Chapter-7: Human Health and Diseases:- Pathogens; parasites causing human diseases (malaria, dengue, chikungunya, filariasis, ascariasis, typhoid, pneumonia, common cold, amoebiasis, ring worm) and their control; Basic concepts of immunology – vaccines; cancer, HIV and AIDS; Adolescence – drug and alcohol abuse.
- Chapter-8: Microbes in Human Welfare:- Microbes in food processing, industrial production, sewage treatment, energy generation and microbes as bio-control agents and bio-fertilizers. Antibiotics; production and judicious use.
Unit-IX Biotechnology and its Applications
- Chapter-9: Biotechnology – Principles and Processes: Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology).
- Chapter-10: Biotechnology and its Applications: Application of biotechnology in health and agriculture: Human insulin and vaccine production, stem cell technology, gene therapy; genetically modified organisms – Bt crops; transgenic animals; biosafety issues, biopiracy and patents.
Unit-X Ecology and Environment
- Chapter-11: Organisms and Populations: Population interactions – mutualism, competition, predation, parasitism; population attributes – growth, birth rate and death rate, age distribution. (Topics excluded: Organism and its Environment, Major Aboitic Factors, Responses to Abioitic Factors, Adaptations)
- Chapter-12: Ecosystem: Ecosystems: Patterns, components; productivity and decomposition; energy flow; pyramids of number, biomass, energy (Topics excluded: Ecological Succession and Nutrient Cycles).
- Chapter-13: Biodiversity and its Conservation: Biodiversity-Concept, patterns, importance; loss of biodiversity; biodiversity conservation; hotspots, endangered organisms, extinction, Red Data Book, Sacred Groves, biosphere reserves, national parks, wildlife, sanctuaries and Ramsar sites.
Uttarakhand Board 12th Biology Practical Syllabus 2024-2025
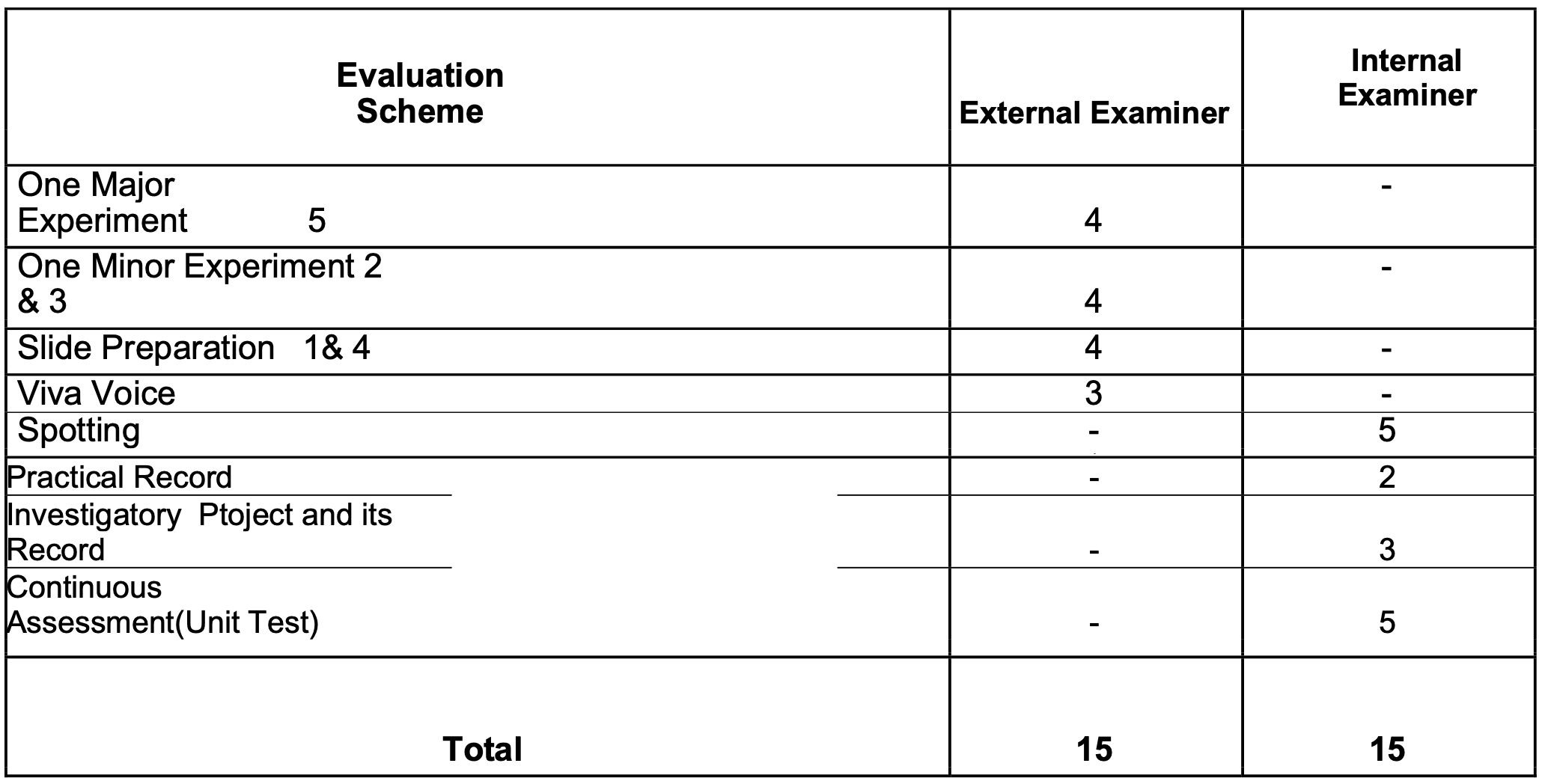
A: List of Experiments:-
- Prepare a temporary mount to observe pollen germination.
- Study the plant population density by quadrat method.
- Study the plant population frequency by quadrat method.
- Prepare a temporary mount of onion root tip to study mitosis.
- Isolate DNA from available plant material such as spinach, green pea seeds, papaya, etc.
B: Study and observer the following (Spotting):-
- Flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies (wind, insects, birds).
- Pollen germination on stigma through a permanent slide or scanning electron micrograph.
- Identification of stages of gamete development, i.e., T.S. of testis and T.S. of ovary through permanent slides (from grasshopper/mice).
- Meiosis in onion bud cell or grasshopper testis through permanent slides.
- T.S. of blastula through permanent slides (Mammalian).
- Mendelian inheritance using seeds of different colour/sizes of any plant.
- Prepared pedigree charts of any one of the genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, blood groups, ear lobes, widow’s peak and colour blindness.
- Controlled pollination – emasculation, tagging and bagging.
- Common disease causing organisms like Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, any fungus causing ringworm through permanent slides, models or virtual images or specimens. Comment on symptoms of diseases that they cause.
C: Models specimen showing symbolic association in root modules of leguminous plants, Cuscuta on host, lichens.
D. Flash cards models showing examples of homologous and analogous organs.
More Links For UBSE Class XII Syllabus 2024-25
| Subject Name (12th) | Subject Code | Syllabus Link |
| 12th Maths | 128 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Physics | 129 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Chemistry | 130 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Biology | 131 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th Hindi | 101 | CLICK HERE |
| 12th English | 103 | CLICK HERE |
| Latest UBSE Updates | UBSE | CLICK HERE |
| UK Board Class 12th All Subjects Syllabus |
All Subjects | CLICK HERE |
| Official Website | UK Board | CLICK HERE |
Frequently Asked Questions:-
Can students expect any questions from environmental issues in the exam?
Yes, the Ecology and Environment section covers important environmental issues, which are likely to be included in the exam. Students should prepare for questions related to biodiversity, pollution, and sustainable development.
What is the weightage of different units in the Biology exam?
The weightage of units varies, with significant emphasis on Genetics, Evolution, and Biotechnology. Reproduction and Ecology also hold considerable importance. The exact distribution can be found in the detailed syllabus provided by the board. 70% theory and 30% practical.
How can students best prepare for the Genetics and Biotechnology sections?
Students should focus on understanding key concepts, practicing problems, and conducting regular revisions. Diagrams and flowcharts can help in retaining information. It's also beneficial to solve past exam papers specifically for these sections.



![UK Board Class 11th Biology Syllabus 2024-2025 [XI UBSE Uttarakhand] feature image](https://4syllabus.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/UK-Board-Class-11th-Biology-Syllabus-2024-2025-XI-UBSE-Uttarakhand-feature-image-150x150.webp)